What is Aerobic Respiration and Why is it Important?
Learn More About Simplified Science PublishingAerobic respiration is important because our cells use this process to convert oxygen and food into the energy that we depend on for life.
Gas exchange may not seem like a thrilling concept, but the ability to exchange gas is the reason why you and nearly every creature on this planet are alive. In particular, our evolutionary ancestors spent at least a billion years perfecting the exchange of two gases: oxygen and carbon dioxide. Almost every cell in your body needs a constant supply of oxygen and also needs to remove carbon dioxide to survive.
Oxygen is essential because our cells use aerobic respiration to convert oxygen and food bits into the energy that we depend on for life. There are many biochemical reactions that create aerobic respiration, but for simplicity’s sake, this article will focus on a central concept: no oxygen = no energy. Organic fuel and other molecules are also required for energy, but oxygen is the only piece of this molecular puzzle that is restocked from outside your body every 4-5 seconds.
What is Aerobic Respiration?
Aerobic respiration is a series of biochemical reactions that convert oxygen and organic fuel into carbon dioxide, water and high-energy molecules. The process starts when organic fuel undergoes digestion in the stomach, intestines, and liver, which are then broken down and transferred into the blood. Oxygen is transferred to the bloodstream via gas exchange in the lungs.
Next, both oxygen and organic fuel move from blood into the body’s cells, where they are used in a series of chemical reactions. These cellular biochemical reactions produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy. Carbon dioxide is transferred back into the blood, water remains inside the cells or moves into other body fluids and high energy molecules usually remain inside the cell it was formed to support the cell’s activity. The full aerobic respiration chemical equation is illustrated below.
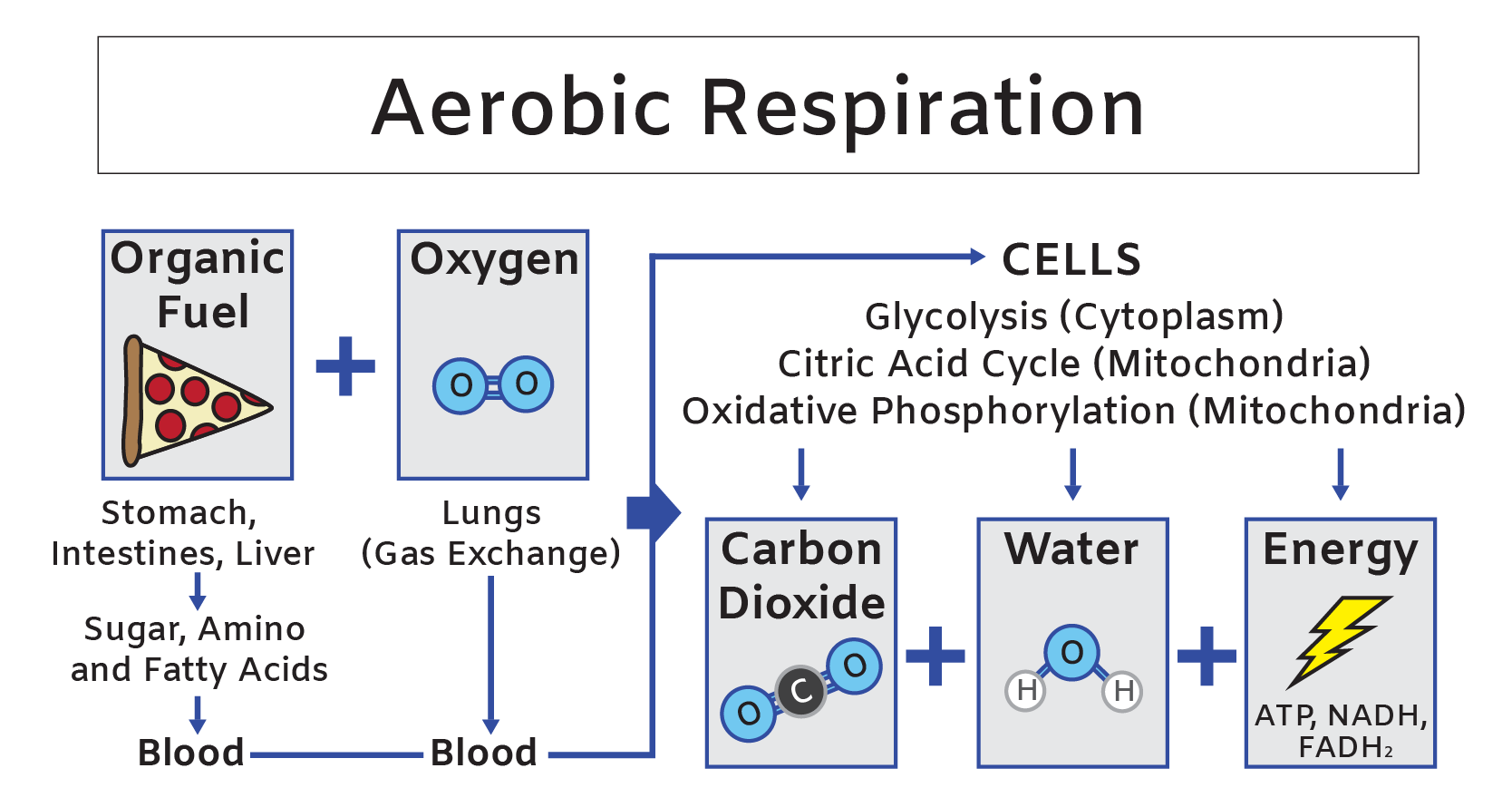
Why is Aerobic Respiration Important?
Aerobic respiration is important because it is the primary way that your cells produce energy. Your cells can also use anaerobic respiration to generate energy without oxygen, but the cellular reactions are less efficient, generate a harmful byproduct called lactic acid and cannot sustain the long-term energy needs of a human cell.
Without aerobic respiration, your cells, (and therefore you), cannot survive more than 10-20 minutes. You can live around three days without water and a week or two without food, but just a few minutes without your cells being able to transform oxygen into energy and the cells in your brain begin to die. This makes aerobic respiration one of the most vital processes that supports your life.
Aerobic Respiration Equation and Summary
Aerobic Respiration: Cells in the human body use aerobic respiration to generate energy, where oxygen and organic fuel are converted into carbon dioxide, water and high-energy molecules.
Aerobic Respiration Equation: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + heat + 38 ATP
For a more detailed review of aerobic respiration, visit: https://biologydictionary.net/aerobic-respiration/
Related Content:
- What is a Heart Attack? Heart Attack Causes and Prevention Tips
- How Does the Heart Work? Review Heart Structure and Function
- What is Blood Made Of? Review Blood Components and Functions
- How Does the Diaphragm Work? Diaphragm Structure and Function
- How Do Lungs Work? Lung Structure and Function
References:
- Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 18th Edition. Longo DL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Jameson J, Loscalzo J. eds.
- Anatomy, Physiology, and Disease: An Interactive Journey for Health Professions , 2nd Edition. Bruce J. Colbert, University of Pittsburgh, Johnstown.
Create professional science figures with illustration services or use the online courses and templates to quickly learn how to make your own designs.
Interested in free design templates and training?
Explore scientific illustration templates and courses by creating a Simplified Science Publishing Log In. Whether you are new to data visualization design or have some experience, these resources will improve your ability to use both basic and advanced design tools.
Interested in reading more articles on scientific design? Learn more below:
Content is protected by Copyright license. Website visitors are welcome to share images and articles, however they must include the Simplified Science Publishing URL source link when shared. Thank you!



